AI in Manufacturing: Key Benefits and Use Cases
AI in manufacturing improves efficiency, enhances product quality, reduces downtime, and supports predictive maintenance, automation, and smarter decision-making

AI in manufacturing is transforming how factories operate by increasing efficiency, improving product quality, and reducing downtime. From predictive maintenance to intelligent automation, AI in manufacturing enables smarter decision-making and faster production cycles. By analyzing data from machines and operations, businesses can streamline processes, identify issues early, and enhance output. As competition grows, integrating AI in manufacturing is no longer optional—it is a strategic move for innovation and long-term success.
What is AI in manufacturing?
AI for manufacturing involves using artificial intelligence in different parts of the production process—like quality checks, supply chain planning, and maintenance. By integrating AI, manufacturers can automate repetitive tasks, make better decisions, improve product quality, and run operations more efficiently. This not only reduces costs and errors but also helps businesses grow by making their processes faster and smarter.
Key Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
-
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI can automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities. This improves overall productivity across the manufacturing floor.
-
Improved Quality Control: Real-time data analysis helps identify defects early, reducing errors and ensuring higher product quality before final delivery.
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI systems can detect signs of equipment failure in advance, enabling timely maintenance and reducing costly downtime.
-
Better Demand Forecasting: AI helps predict future demand by analyzing historical sales and market trends, supporting better inventory and production planning.
-
Cost Savings: Through automation and improved efficiency, AI reduces labor and operational costs, helping companies maintain better profit margins.
-
Enhanced Safety: AI-powered robots can take on hazardous tasks, minimizing workplace injuries and ensuring a safer environment for human workers.
-
Real-Time Data Analysis: AI processes massive volumes of data instantly, offering insights that help manufacturers make informed, quick decisions.
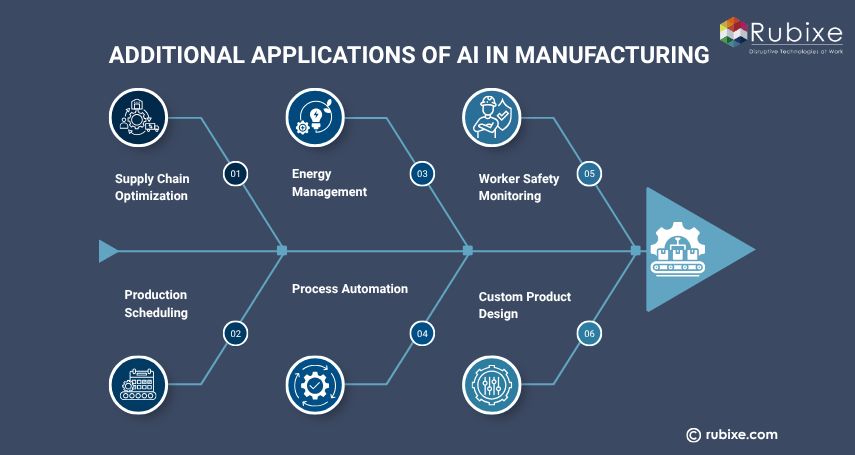
Additional Applications of AI in Manufacturing
Beyond predictive maintenance and quality control, AI is reshaping many areas of modern manufacturing by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling smarter operations. Here are some expanded applications:
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI algorithms analyze supplier data, demand forecasts, and logistics to streamline inventory and reduce delays.
-
Production Scheduling: Intelligent systems dynamically adjust schedules based on real-time data like machine availability, material flow, or workforce constraints.
-
Energy Management: AI helps monitor and reduce energy consumption across manufacturing units, contributing to sustainability goals.
-
Computer Vision for Defect Detection: Advanced visual inspection systems powered by AI catch defects that human eyes or traditional sensors might miss.
-
Process Automation: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) paired with AI automates repetitive tasks such as order processing, reporting, or compliance tracking.
-
Worker Safety Monitoring: AI-enabled sensors and cameras track workplace conditions to prevent accidents or identify risky behaviors.
-
Custom Product Design: AI tools assist in generative design and rapid prototyping, enabling faster development of customized products.
Key AI Segments That Impact Manufacturing
AI in manufacturing is not limited to one technology—it spans a range of intelligent capabilities that support efficiency, precision, and innovation across operations. Several core segments are making a notable impact:
-
Machine Learning: Uses algorithms to identify patterns in manufacturing data and improve performance over time without manual intervention. Common applications include predictive maintenance, defect detection, and demand forecasting.
-
Deep Learning: A more advanced form of machine learning that uses neural networks to process complex inputs like images, video, and sensor data. This is especially useful in visual inspection systems and quality assurance.
-
Autonomous Objects: Includes collaborative robots (cobots), autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), and smart machinery that can make real-time decisions, optimize routes, and adapt to changing environments with minimal human input.
How Is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
Artificial intelligence is reshaping manufacturing by enabling smarter, faster, and more autonomous systems. Here are some of the core ways AI is applied in this sector:
-
Learning from Human Demonstration: AI systems can observe how humans perform a task and then replicate it. Over time, they improve through repetition and can handle complex tasks without direct supervision, improving both efficiency and scalability.
-
Crowdsourced Training Data: By leveraging data gathered from a broad group of sources—such as user input, machine feedback, or online repositories—AI systems gain access to collective insights. This enhances their decision-making and expands their learning capacity beyond a single environment.
-
Unsupervised and Reinforcement Learning: AI in manufacturing often uses unsupervised learning to recognize patterns in unlabeled data. Through reinforcement learning, these systems learn by trial and error, continuously adjusting their actions to optimize outcomes such as reduced downtime or energy use.
The Impact of AI on Industrial Operations
-
Preventing Future Problems: AI helps manufacturers predict when equipment might fail. This allows them to schedule maintenance and repairs ahead of time, reducing unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime.
-
Creative Generating: Generative design uses machine learning to simulate how engineers design products. This approach can create hundreds of design variations quickly, giving manufacturers more options to choose from.
-
Forecasting Raw Material Prices: AI-powered tools can predict the prices of raw materials more accurately than humans. These systems also learn and improve over time, making their forecasts even better.
-
Edge Analytics: By analyzing data from machine sensors on-site, AI delivers faster insights without needing to send information to a central system. This helps in making quicker decisions on the factory floor.
-
Quality Controls: AI systems with machine vision can identify flaws in products by detecting anything that looks out of the ordinary. This helps maintain consistent quality in manufacturing.
-
Robotics: Manufacturing robots handle repetitive tasks, reduce mistakes, and allow human workers to focus on more valuable activities. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
-
Process Improvement: AI tools help optimize manufacturing processes, making it easier for companies to achieve long-term, sustainable production goals.
AI Services helps manufacturers improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality using smart technologies. With AI-driven tools for automation and maintenance, we support businesses in streamlining operations and staying competitive